Crop Factor Explained: Mastering Its Role in Photography
Understanding the concept of crop factor is crucial for photographers, as it affects both the focal length and field of view of a lens. Crop factor refers to the ratio of a camera sensor's size to a 35mm film frame. This information helps photographers choose the right lenses for their cameras, as well as calculate effective focal lengths when comparing lenses between different DSLRs.
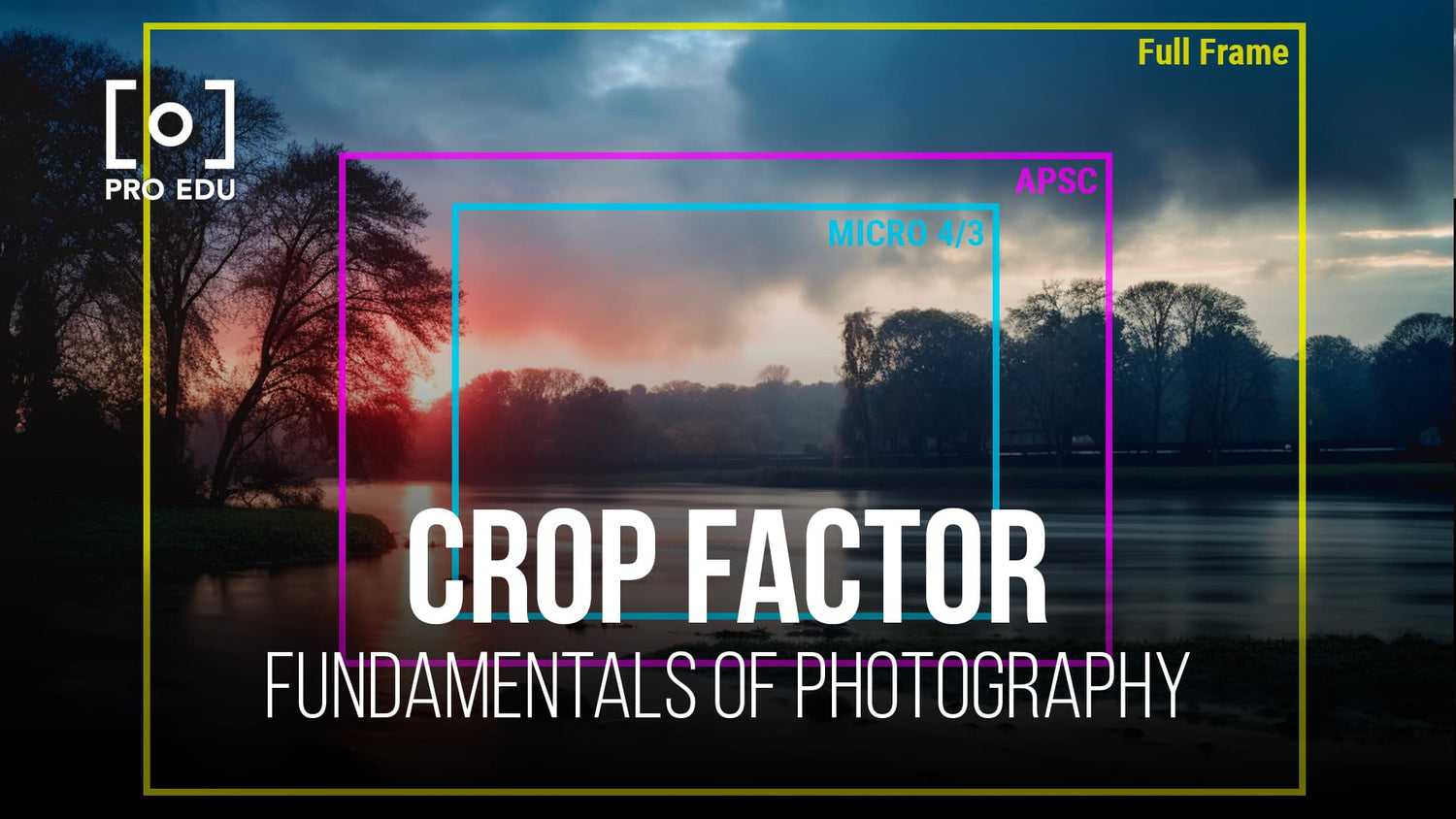
The impact of crop factor on photography depends on the camera brand and sensor size, which can vary significantly. For instance, full-frame cameras have a crop factor of 1, while cameras with APS-C and Micro Four Thirds sensors have higher crop factors. This variation changes the effective focal length of lenses, affecting how wide or narrow the field of view is in your images.
Key Takeaways
- Crop factor is a crucial concept in photography, as it impacts the focal length and field of view of lenses.
- Understanding crop factor helps photographers make informed lens choices for their cameras.
- Sensor size and camera brand can influence the crop factor, affecting the practical implications of crop factor on photography.
Understanding Crop Factor
Crop factor is a term used in photography to describe the difference between a camera's sensor size and a traditional 35mm film frame. This concept is important as it helps us understand how a particular lens will perform when mounted on cameras with different sensor sizes, such as full-frame or APS-C cameras.
In the world of photography, full-frame sensors are considered the reference point since they are the same size as a 35mm film frame1. Cameras that have smaller sensors than full-frame, like the APS-C sensor, will have a crop factor greater than 12. This means that the field of view captured by the lens will be smaller than if it were mounted on a full-frame camera.
To calculate crop factor, we can divide the diagonal length of the full-frame sensor (43.27mm) by the diagonal length of the crop sensor3. For example, if an APS-C sensor has a diagonal length of 28.21mm, the crop factor will be approximately 1.534.
When using a crop sensor camera, it's crucial to consider the impact of the crop factor on the effective focal length of the lens. To do this, we simply multiply the actual focal length of the lens by the crop factor5. Let's say we have a 50mm lens on an APS-C camera with a crop factor of 1.5; the effective focal length would become 75mm, which translates to a narrower field of view.
In conclusion, the concept of crop factor is essential for photographers to understand how their lenses will perform on various camera bodies. By taking sensor size and crop factor into account, we can make informed decisions when selecting lenses and anticipate the resulting field of view in our images.
Crop Factor and Focal Length
Impact on Field of View
Crop factor is a term that describes the difference between a camera sensor's size and a traditional 35mm film frame. When using lenses on different sensor sizes, the field of view changes due to the crop factor. For example, a 50mm lens on a camera with a 1.5x crop factor will have a field of view equivalent to a 75mm lens on a full-frame camera.
The smaller the sensor, the narrower the field of view will be, affecting the way our images look. This can be both a blessing and a curse depending on the type of photography we're doing. For instance, it can be useful when shooting wildlife or sports, where a longer focal length is advantageous.
Equivalent Focal Length
To understand the impact of crop factor on focal length, we can calculate the equivalent focal length by simply multiplying the crop factor by the lens focal length. For example, a 50mm lens on a camera with a 1.5x crop factor will have an effective focal length of 75mm (50mm x 1.5 = 75mm).
Using equivalent focal lengths helps us better compare lenses between camera systems and understand how different sensor sizes affect our images. It's important to note that the actual focal length of the lens doesn't change, but rather the field of view is affected by the crop factor.
In conclusion, understanding crop factor and its impact on focal length is crucial for photographers who want to get the most out of their equipment. By knowing how crop factor affects field of view and equivalent focal length, we can make more informed decisions when choosing lenses and camera systems for our specific needs.
Implications of Crop Factor on Lens Choices
When considering lenses for your camera, it's important to understand how crop factor impacts your lens choices. In this section, we'll discuss the implications of crop factor on both zoom lenses and telephoto lenses.
Zoom Lenses
Zoom lenses are versatile as they cover a range of focal lengths, making them suitable for various situations. However, when using a camera with a crop sensor, the effective focal length of the lens changes. For instance, a 24-70mm lens used on a camera with a 1.5x crop factor would have an effective focal length of 36-105mm. This could limit the ability to achieve wide-angle shots, which might require investing in a wider zoom lens specifically designed for crop sensors.
Telephoto Lenses
For telephoto lenses, the crop factor can actually work to our advantage. Since the effective focal length increases, it can help us get closer to subjects without purchasing a longer telephoto lens. For example, using a 200mm lens on a 1.5x crop sensor camera would yield an effective focal length of 300mm, giving us more reach without spending additional money on a longer lens.
In conclusion, understanding how crop factor affects your lens choices is essential for making the best decisions when investing in photographic equipment. Keep these implications in mind when selecting lenses for your camera, and you'll be well-equipped to capture stunning images regardless of the situation.
Crop Factor Across Different Camera Brands
Nikon DX and FX
Nikon offers two sensor formats in their DSLR cameras: DX and FX. DX format uses an APS-C sensor with a 1.5x crop factor, while FX format corresponds to a full-frame sensor with no crop factor. The crop factor impacts focal length, depth of field, and field of view. Nikon DX cameras are typically more compact, lightweight, and cost-effective, whereas FX provides better low-light performance and overall image quality.
Canon APS-C and Full-Frame
Similar to Nikon, Canon offers both APS-C and full-frame sensors in their range of cameras. Canon's APS-C sensors have a slightly different crop factor than Nikon, at 1.6x. This means that an equivalent lens on a Canon APS-C camera would have a marginally longer effective focal length than on a Nikon DX camera. Full-frame Canon cameras offer better low-light performance, image quality, and a larger field of view than their APS-C counterparts. You can learn more about Canon's crop factors here.
Sony and Panasonic Micro Four Thirds
Unlike Nikon and Canon, Sony and Panasonic offer another sensor format: Micro Four Thirds (MFT). This standard was created by Olympus and Panasonic and is now used by multiple brands. MFT cameras have a 2x crop factor, meaning a 25mm MFT lens would behave like a 50mm full-frame lens. Though MFT sensors are smaller than APS-C and full-frame sensors, they provide a good balance of portability and image quality. Some advantages of MFT cameras include smaller lens sizes, lighter overall weight, and impressive video capabilities. For more information on Micro Four Thirds cameras, check out this article.
In summary, it's essential to be aware of the crop factor when choosing a camera and lens combination, as it affects focal length, depth of field, and field of view. By understanding these differences across various camera brands, we can make informed decisions and select the gear that best meets our photography needs.
Practical Implications of Crop Factor on Photography
When considering the impact of crop factor on photography, there are several elements to take into account. For instance, depth of field, image quality, and resolution are all affected by the crop factor to some extent.
Using a camera with a higher crop factor, such as an APS-C sensor found in many DSLR and mirrorless cameras, will result in a narrower field of view compared to a full-frame camera. This means that a given lens will effectively have a longer focal length on a crop sensor camera.
Depth of field: Crop sensor cameras typically give the appearance of a deeper depth of field for a given aperture, compared to full-frame cameras. This can be either an advantage or a disadvantage, depending on the desired outcome for the photo.
Image quality: While crop sensors have improved significantly over the years, full-frame sensors generally provide better overall image quality, particularly in low light situations. However, for many photographers, the image quality difference may not be significant enough to justify the increased cost and size of a full-frame camera.
Resolution: The resolution of a camera depends on its sensor size, pixel size, and pixel count. Generally, full-frame cameras offer higher resolution than crop sensor cameras. However, there are crop sensor cameras that offer a competitive resolution and overall quality when compared to some full-frame cameras.
With the rise of mirrorless cameras, many manufacturers are offering both full-frame and crop sensor options, giving photographers more choices to suit their needs and preferences. No matter which type of camera you choose, understanding the implications of crop factor in photography is essential to make the most of your gear and capture the images you envision.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does crop factor influence field of view?
Crop factor affects the field of view by changing the angle of view captured by the camera. A smaller sensor has a narrower field of view than a larger one. Essentially, the larger the crop factor, the more the image will be cropped, leading to a narrower field of view.
Does crop factor impact depth of field?
Yes, crop factor does influence depth of field. A camera with a smaller sensor will have a deeper depth of field compared to a full-frame camera, given the same aperture and framing. This is because smaller sensors require the use of shorter focal length lenses to achieve the same framing, resulting in a deeper depth of field.
What is the relationship between crop factor and focal length?
Crop factor is a tool for understanding the effective focal length of a lens when used on a camera with a smaller sensor. The effective focal length is calculated by multiplying the lens's actual focal length by the crop factor. This helps photographers compare lenses and understand how they will perform on different sensor sizes.
How do different sensor sizes relate to crop factors?
Different sensor sizes have different crop factors, which determine how the field of view changes compared to a full-frame sensor. Full frame sensors have a crop factor of 1, while smaller sensors like APS-C have a crop factor around 1.5 to 1.6. Micro Four Thirds cameras have a crop factor of 2. The larger the crop factor, the smaller the sensor.
Does crop factor affect the apparent sharpness in photographs?
Crop factor can impact the apparent sharpness of a photo, particularly when using lenses designed for full-frame cameras on smaller sensors. This is because when you crop the image, you are effectively magnifying the central part of the image, potentially revealing more detail or flaws in the image. However, using a lens designed for the specific crop sensor size can help maintain sharpness.
What role does crop factor play in lens compatibility?
Crop factor plays an important role in understanding lens compatibility for cameras with different sensor sizes. Lenses designed for full-frame cameras can generally be used on smaller sensor cameras, but with an effective focal length change due to the crop factor. Conversely, using a lens designed for a smaller sensor on a full-frame camera may result in vignetting or loss of image quality. Understanding crop factor can help you choose the most appropriate lenses for your camera system.